- Data breaches, attacks on critical infrastructure or physical assets and increased ransomware attacks drive cyber concerns globally and in Africa for 2024.
- Business interruption remains #2 with 31%. ‘Natural catastrophes’ is the biggest riser compared to 2023 with 26% in #3
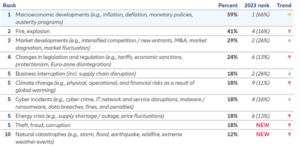
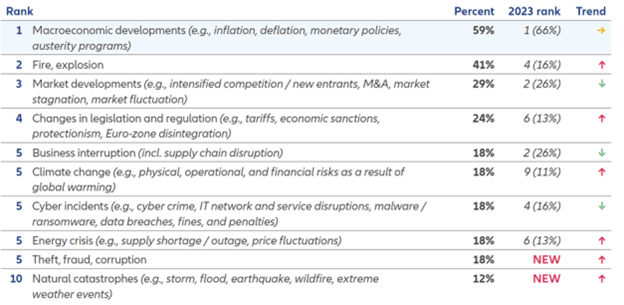
- In Ghana, ‘Macroeconomic developments’ such as inflation remained the topmost business risk concern, followed closely by fire and explosion, rising to the second position in this year’s rankings.
Cyber incidents, such as ransomware attacks, data breaches and IT disruptions, are the biggest worry for companies globally in 2024, according to the Allianz Risk Barometer. The closely interlinked peril of business interruption ranks second. Natural catastrophes (up from #6 to #3 year-on-year), Fire, explosion (up from #9 to #6), and Political risks and violence (up from #10 to #8) are the biggest risers in the latest compilation of the top global business risks, based on the insights of more than 3,000 risk management professionals.
Top three risks in Ghana for 2024
In Ghana, Macroeconomic developments, once again takes centre-stage as the most concerning business risk. This is no surprise due to Ghana’s current economic challenges, which resulted in the government’s request for a US$3billion (about US$9 per person in the US) bail-out from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in 2023. Following closely in second place is Fire, explosion (up from fourth place last year) and Market developments in third place.
Ababacar Diaw, CEO of Allianz Insurance Ghana, believes that it is imperative now more than ever that companies build capacity to remain resilient to business shocks through the strategic planning and implementation of business continuity measures, which include the use of insurance covers. “The findings published in the 2024 Allianz Risk Barometer report indicate that Macroeconomic developments are the foremost concern of businesses and business leaders in the country due to Ghana’s current economic challenges. As business leaders, it is paramount that we join forces and take vital steps to find the best solutions to these occurring and emerging risks. Cyber risk is also surging with the increase in Internet penetration. Thus, strategies centred on resilience, risk mitigation and business continuity must be prioritised. This is one of the reasons why the insurance industry exists and companies like Allianz Insurance are continually researching the business community to develop tailor-made solutions that mitigate the impact of these risks,” he opined.
A cyber event is the top global business risk for 2024 in Africa and the Middle East
In Africa and the Middle East, cyber incidents have emerged as the most significant concern for businesses in 2023, climbing from the second position in the previous year. Business interruption, which held the third position in 2022, has now moved up to the second spot in the region. Macroeconomic developments dropped to the third position after holding the top spot last year. This shift reflects the evolving economic landscape in Africa and the Middle East, and the challenges businesses face in navigating uncertain market conditions.
Allianz Commercial CEO Petros Papanikolaou comments on the findings: “The top risks and major risers in this year’s Allianz Risk Barometer reflect the big issues facing companies around the world right now – digitalisation, climate change and an uncertain geopolitical environment. Many of these risks are already hitting home, with extreme weather, ransomware attacks and regional conflicts expected to test the resilience of supply chains and business models further in 2024. Brokers and customers of insurance companies should be aware and adjust their insurance covers accordingly”.
Large corporates, mid-size and smaller businesses are united by the same risk concerns – they are all mostly worried about cyber, business interruption and natural catastrophes. However, the resilience gap between large and smaller companies is widening, as risk awareness among larger organisations has grown since the pandemic with a notable drive to upgrade resilience, the report notes. Conversely, smaller businesses often lack the time and resources to identify and effectively prepare for a wider range of risk scenarios and, as a result, take longer to get the business back up and running after an unexpected incident.
Trends driving cyber activity in 2024
Cyber incidents (36 percent of overall responses) rank as the most important risk globally for the third year in a row – for the first time by a clear margin (5 percent points). Cyber incidents ranks #5 in Ghana down from #4 in 2023. It is the top peril in 17 countries, including Uganda, Kenya, Mauritius, Germany, India, Japan, the UK, and the USA. A data breach is seen as the most concerning cyber threat for Allianz Risk Barometer respondents (59 percent) followed by attacks on critical infrastructure and physical assets (53 percent). The recent increase in ransomware attacks – 2023 saw a worrying resurgence in activity, with insurance claims activity up by more than 50 percent compared with 2022 – ranks third (53 percent).
“Cyber criminals are exploring ways to use new technologies such as generative artificial intelligence (AI) to automate and accelerate attacks, creating more effective malware and phishing. The growing number of incidents caused by poor cyber-security, in mobile devices in particular, a shortage of millions of cyber security professionals, and the threat facing smaller companies because of their reliance on IT outsourcing are also expected to drive cyber activity in 2024,” explains Scott Sayce, Global Head of Cyber, Allianz Commercial.
Business interruption and natural catastrophes
Despite an easing of post-pandemic supply chain disruption in 2023, Business interruption (31 percent) retains its position as the second biggest threat in the 2024 survey. Business interruption ranks in the top five risks in Ghana, Kenya, Senegal, South Africa and Uganda. This result reflects the interconnectedness in an increasingly volatile global business environment, as well as a strong reliance on supply chains for critical products or services. Improving business continuity management, identifying supply chain bottlenecks, and developing alternative suppliers continue to be key risk management priorities for companies in 2024.
‘Natural catastrophes’ (26 percent) is one of the biggest movers at #3, up three positions globally and features as new risk in Africa and the Middle East (#6) and Ghana (#10). 2023 was a record-breaking year on several fronts. It was the hottest year since records began, while insured losses exceeded US$100bn for the fourth consecutive year, driven by the highest-ever damage bill of US$60bn from severe thunderstorms. In Africa and the Middle East, natural catastrophes have emerged as a new risk, ranking at #6. Notably, Morocco witnessed a significant rise in this risk, climbing from seventh to first place. Cameroon and South Africa also experienced a surge in natural catastrophe risks, ranking among the top five risks in these countries.
Regional differences and risk risers and fallers
Climate change (18 percent) may be a non-mover year-on-year at #7, but is among the top three business risks in countries such as Brazil, Greece, Italy, Turkey and Mexico. Climate change dropped from fourth to tenth place in Africa and the Middle East compared to the previous year. However, it remains a top-five concern in countries such as Ghana, Mauritius, Morocco and Nigeria. Physical damage to corporate assets from more frequent and severe extreme weather events is a key threat. The utility, energy and industrial sectors are among the most exposed. In addition, net zero transition risks and liability risks are expected to increase in the future as companies invest in new, largely untested low-carbon technologies to transform their business models.
Unsurprisingly, given ongoing conflicts in the Middle East and Ukraine, and tensions between China and the US, ‘Political risks and violence’ (14 percent) is up to #8 from #10. Interestingly, this risk has moved down one place to seventh in Africa and the Middle East, while ranking as one of the top five risks in Cameroon and Ivory Coast. 2024 is also a super-election year, where as much as 50 percent of the world’s population could go to the polls, including in Ghana, Mauritius, Senegal, South Africa, India, Russia, the US, and the UK. Dissatisfaction with the potential outcomes, coupled with general economic uncertainty, the inflated cost of living, and growing disinformation fuelled by social media, means societal polarisation is expected to increase, triggering more social unrest in many countries.
However, there is some hope among Allianz Risk Barometer respondents that 2024 could see the wild economic ups and downs experienced since the COVID-19 shock settle down, resulting in ‘Macroeconomic developments’ (19 percent) falling to #5 from #3 globally and moves down to #3 from #1 in Africa and the Middle East. It ranks as the #1 risk in Ghana, Cameroon, Mauritius and Nigeria. Yet economic growth outlooks remain subdued – just over 2 percent globally in 2024, according to Allianz Research.
“But this lacklustre growth is a necessary evil: high inflation rates will finally be a thing of the past,” says Ludovic Subran, Chief Economist at Allianz. “This will give central banks some room to manoeuver – lower interest rates are likely in the second half of the year. Not a second too late, as stimulus cannot be expected from fiscal policy. A caveat is the considerable number of elections in 2024 and the risk of further upheavals depending on certain outcomes.”
In a global context, the shortage of skilled workforce (12 percent) is seen as a lower risk than in 2023, dropping from #8 to #10. However, businesses in Central and Eastern Europe, the UK and Australia identify it as a top five business risk. Given there is still record-low unemployment in many countries around the globe, companies are looking to fill more jobs than there are people available to fill them. IT or data experts are seen as the most challenging to find, making this issue a critical aspect in the fight against cyber-crime.
Top 10 Risks in Ghana for 2024