- Background to Cedi’s recent performance
The Ghanaian cedi has long been characterised by persistent volatility, often undermining economic stability and investor confidence. For years, the currency has been on a steady downward trajectory against major international currencies such as the US dollar, British pound, euro, and Japanese yen. The 2024 fiscal year was particularly difficult for the cedi, with the local currency ranked among the four worst-performing currencies in Sub-Saharan Africa, according to the World Bank’s Africa Pulse report published in October 2024. During the same period, the cedi had depreciated by approximately 24% against the US dollar. Just two months earlier, Bloomberg similarly listed the cedi as one of the world’s worst-performing currencies.
The consequences of this sustained depreciation were severe. The sharp decline in the cedi’s value eroded public trust in the national currency and strained the broader economy. Vulnerable populations bore the brunt of the impact, as the rising cost of living significantly diminished household purchasing power. Inflation surged, driven largely by increased prices of essential goods and services, compounding the financial hardships faced by many Ghanaians.
However, in a notable shift, recent months have seen a marked appreciation of the cedi. This paper examines the policy implications of this reversal, an unusual but welcome development in Ghana’s macroeconomic landscape. It seeks to analyse the drivers behind the cedi’s recent appreciation, its effect on the economy, assess its potential sustainability, and explore how policymakers can leverage this momentum to enhance macroeconomic stability and support inclusive growth.
- The Cedi’s Performance against major currencies over the past year
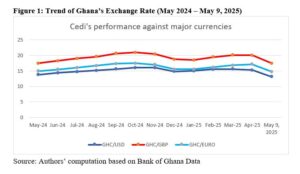
The Ghanaian cedi has demonstrated a remarkable turnaround, shifting from one of Sub-Saharan Africa’s worst-performing currencies in 2024 (World Bank, 2024) to the best-performing currency globally in 2025, with a nearly 16% appreciation against the US dollar (Bloomberg, 2025). Data from the Bank of Ghana’s interbank exchange rates indicate that the cedi experienced sharp depreciation during August to October 2024. However, by the close of the year, the currency began to stabilize. This positive momentum has largely continued through 2025, aside from a brief dip in February, and reflects renewed market confidence, stronger macroeconomic fundamentals, and ongoing policy reforms.
Figure 1: Trend of Ghana’s Exchange Rate (May 2024 – May 9, 2025)
- What are the underlying drivers of the Cedi’s appreciation
The recent appreciation of the Ghanaian cedi is driven by a combination of factors, with varying degrees of impact. While some contributors exert only marginal influence, others play a more substantial role in strengthening the local currency. Understanding the relative weight of these drivers is essential for evaluating the sustainability of the cedi’s current performance.
- Accumulation of gold reserves
A key driver behind the recent appreciation of the cedi is the continued accumulation of gold reserves by the Bank of Ghana. Between May 2024 and April 2025, the Central Bank increased its gold holdings by 40.6%, rising from 22.3 tonnes to 31.2 tonnes. This significant buildup strengthens the intrinsic value backing the cedi and enhances the country’s reserve adequacy. By anchoring part of its reserves in gold, a globally trusted store of value, the Bank of Ghana sends a strong signal of its capacity to support the cedi and manage volatility. This move also reinforces market confidence that the central bank is well-positioned to counter speculative pressures when necessary.
- Government fiscal operations
The cedi’s recent appreciation can also be attributed to the government’s improved fiscal management. Significant expenditure cuts aimed at promoting fiscal discipline and consolidation have reinforced confidence in the economy. These measures have been complemented by the elimination of certain distortionary taxes, including the E-levy, betting tax, and COVID-19 levy, thereby improving the fiscal outlook and easing burdens on businesses and consumers.
In addition, the government’s steadfast commitment to the IMF-supported reform agenda, which recently led to a staff-level agreement expected to unlock $370 million in financial support, has further strengthened investor sentiment. This policy consistency has helped reduce negative market speculation and the associated pressure on foreign exchange demand.
These fiscal efforts have received international validation through S&P Global Ratings’ recent upgrade of Ghana’s foreign-currency sovereign credit rating from Selective Default (SD) to CCC+, reflecting a more favorable perception of the country’s fiscal and external positions.
- Improved export earning from Gold and Cocoa
The cedi’s appreciation is partly driven by increased export revenues from surging gold and cocoa prices on the international market. As a major exporter of both commodities, Ghana has benefited significantly, most notably from gold, which rose from around US$2,000 to approximately US$3,400 per ounce by May 2025. This price rally generated an estimated US$11.6 billion in gold export revenues in 2024, up from US$7.6 billion in 2023, with further gains expected in 2025. Cocoa prices have also remained elevated despite recent volatility.
These increased forex inflows have strengthened dollar supply, easing pressure on the cedi. Additionally, the formalisation of the small-scale gold mining sector has led to a notable rise in export volumes, further boosting foreign exchange earnings and supporting currency stability.
- Minimised foreign debt servicing
A key factor easing pressure on the cedi is the temporary suspension of external debt servicing under Ghana’s ongoing Debt Restructuring Programme. Since the last payment in January 2025, the government has paused foreign currency-denominated debt repayments, with the next scheduled payment due in July 2025. This break has reduced the demand for forex typically required to meet debt obligations, thereby alleviating downward pressure on the cedi in the interim.
- Weakening US Dollar
The recent depreciation of the US dollar driven by investor uncertainty over newly imposed reciprocal tariffs and fears of a potential recession has eased global demand for the currency. For Ghana, this shift has reduced external exchange rate pressures, contributing to the cedi’s relative stability and recent appreciation.
- How Cedi appreciation is shaping Ghana’s economic outlook
The recent appreciation of the cedi is influencing Ghana’s economic outlook in complex ways. While a stronger currency brings several benefits such as reduced import costs and lower inflationary pressures, it also presents challenges, particularly for export competitiveness and revenue projections. Understanding these mixed effects is essential for assessing the broader implications of currency stability on the country’s macroeconomic trajectory.
- Reduced imported inflation
The appreciation of the cedi has helped ease imported inflation in Ghana’s highly import-dependent economy by lowering the cost of foreign goods and reducing pressure on foreign exchange demand. This has contributed to price stability and supported the Bank of Ghana’s disinflation efforts, as reflected in the decline in inflation from 23.8% in December 2024 to 21.2% in April 2025.
- Improved external debt management
Ghana’s debt burden stems from both external and domestic sources, with external debt accounting for over half of the total. According to the 2025 Budget Statement and Economic Policy, as of December 2024, the country’s total public debt stood at US$49.3 billion, of which US$28.3 billion was external. The recent appreciation of the cedi has helped ease the cost of servicing external debt by making repayments cheaper in local currency terms. This development supports improved debt sustainability and reduces fiscal pressure on the economy.
- Strengthening foreign reserves and investor confidence
The appreciation of the cedi reduces the need for the Bank of Ghana to intervene frequently in the foreign exchange market by selling large volumes of foreign reserves to stabilise the currency. This easing of intervention pressure supports the accumulation and preservation of foreign reserves. Moreover, a stable and strengthening currency enhances investor confidence, encouraging capital inflows that can stimulate economic growth and reinforce macroeconomic stability.
- Increased lending to the Real Sector
A stronger cedi reduces speculative demand for foreign currency, easing pressure on the forex market and improving liquidity within the financial sector. With reduced “panic-buying” and currency volatility, financial institutions are better positioned to extend credit. Additionally, the ongoing decline in government treasury bill (T-bill) rates is reducing the attractiveness of lending to the public sector. This shift is likely to incentivise banks to channel more funds toward the productive, real sectors of the economy – supporting investment, job creation, and overall economic growth.
- The economic trade-offs of Cedi appreciation
While a stronger cedi offers macroeconomic benefits, it may also reduce the competitiveness of Ghanaian goods both domestically and internationally. The recent imposition of a 10% U.S. tariff on Ghanaian exports, combined with the cedi’s appreciation, makes Ghanaian products relatively more expensive abroad, posing a risk to export revenues. Domestically, the appreciation lowers the cost of imported goods, making them more attractive compared to locally produced alternatives, especially where local production depends on imported inputs. This shift in consumer preference toward imports can widen the trade deficit and undermine domestic industry performance, with potential implications for GDP growth.
- Recommendations
To ensure that the recent appreciation of the cedi is sustained and not short-lived, CERPA recommends the following strategic policy actions to the Bank of Ghana and the Government of Ghana.
- Strengthen macroeconomic stability
The government should maintain prudent fiscal management and reduce the fiscal deficit through disciplined spending and enhanced domestic revenue mobilisation. A credible commitment to macroeconomic stability builds investor confidence and supports a stronger currency.
- Encourage retention and reinvestment of foreign profits
The government should consider strategies to incentivise foreign investors to reinvest a portion of their earnings locally rather than fully repatriating profits. This would reduce excessive demand for foreign currency and support cedi stability.
- Promote import substitution and domestic production
Reducing reliance on imports through policies that support local industries particularly in agriculture and manufacturing can ease pressure on the cedi. Providing incentives for local production will help correct trade imbalances and strengthen the domestic economy.
- Strengthen the Gold Purchase Programme to bolster foreign reserves
The government and the Bank of Ghana should reinforce the gold purchasing programme as a strategic tool to increase the country’s gold reserves. A stronger reserve position provides intrinsic backing for the cedi, enhances the central bank’s capacity to respond to exchange rate pressures, and serves as a long-term buffer against external shocks thereby supporting sustained currency stability.
- Adopt targeted monetary policies
The Central Bank should implement interest rate and liquidity management policies aimed at maintaining low and stable inflation. By keeping inflation under control, real returns on investments are preserved, thereby attracting both domestic and foreign investors.
- Boost foreign exchange reserves through FDI and export diversification
Ghana must prioritise attracting long-term foreign direct investment (FDI) by ensuring political and economic stability, improving the business environment, and offering competitive investment incentives. Simultaneously, increasing the volume and value of exports, particularly through value addition and product diversification can enhance foreign exchange earnings.










