By Professor Ernest Ofori ASAMOAH
The concept of social enterprise is reshaping the way businesses operate, blending profit-making with a strong commitment to social and environmental impact.
All over the world, social enterprises are proving that businesses can do good while remaining financially sustainable.
Non-profit Organizations (NPOs) and Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) are typically established to address a variety of societal needs; whether social, environmental, economic, cultural or psychological.
The core mission of NPOs and NGOs is not to generate profit (money); instead, any income they produce is reinvested into their efforts to achieve their goals.
These organizations do not distribute profits to their members or founders. Their primary aim is to do good for society and solve pressing social challenges.
On the other hand, profit-making businesses exist primarily to generate profit. While they may address social issues through corporate social responsibility (CSR) or corporate social investment (CSI), these initiatives are secondary to their main goal of making profit.
Despite the growing focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) issues, businesses remain fundamentally profit-driven.
Social enterprise as a business model, however, provides a middle way of doing good (solving social and environmental challenges) and making money (profit objective).

The Social Enterprise Business Model
Social enterprises are businesses that apply commercial principles to address social and environmental challenges. In essence, they operate with both social and environmental objectives, alongside a traditional business goal.
There are three key attributes that typically define a social enterprise: its business objectives, its entrepreneurial model, and its governance structure.
The primary aim of a social enterprise is to tackle specific social or environmental issues within communities or society at large. These issues could range from healthcare challenges and waste management to food security, environmental degradation, or global warming.
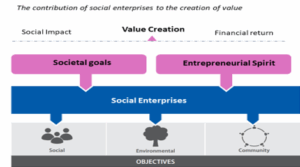
The social objective of a social enterprise should be compelling enough to drive entrepreneurial ventures, enabling them to achieve economic independence and long-term sustainability.
These ventures must generate sufficient revenue to cover their operations, reducing their reliance on grants and donations. Moreover, for a business to be considered a social enterprise, it must have inclusive and participatory governance.
The focus should be on the interests of all stakeholders and beneficiaries, rather than solely on the interests of the owners or shareholders.
It is estimated that there are approximately eleven million social enterprises worldwide, operating in various legal forms. These enterprises have a broad range of impact, from global initiatives to local projects, and span across every sector of the economy, including but not limited to agriculture, education, healthcare, food, arts, and more.
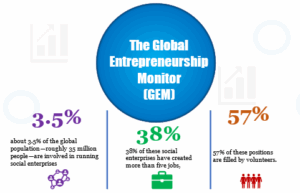
The Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) estimates that about 3.5% of the global population—roughly 35 million people—are involved in running social enterprises. Additionally, 38% of these social enterprises have created more than five jobs, and 57% of these positions are filled by volunteers.
>>>the writer is with Regent University College of Science and Technology. He can be reached via [email protected]