…. aligning operational strategy and innovation for cultural excellence and operational profitability.
For most businesses, operational success is not a random occurrence but rather a series of right decisions taken at the right instances. Meticulous planning, preparation and execution serve as panacea for success for most organizations.
With these, start with defining the right strategy and the adherence of discipline to make the strategy work. By this, organizations think of competing for market dominance, profitability and remain excellent in operations with its portfolio of products and services by taking the steps to examine the effectiveness and efficiency of its operational systems and how it supports the quest to achieve its corporate objectives.
The lack of a clear strategy for operations and the alignment of supportive systems, practices and culture is a recipe for organizational failure. Notably, the effective operational strategy encompassing the creative ability of the organization to remain genuinely creative and innovative with its products and services guarantee a differential advantage over its competitors.
Hence, the delivery of great products and services backed by robust systems to support operational and cultural excellence remain a strategic and a tactical operational issue rather than an adhoc or random operational decision. I therefore submit to deal with the underpinning factors and strategies that contribute to operational and cultural excellence of any organization. Let’s talk operational strategy.
Why do organizations fail?
To begin with, it is a fact that not all organizations are sound, resilient enough to weather the storms of market competitions and positioning. Those organizations may also suffer profitability and diverse issues of systemic, reputational and cultural risks as well. Therefore, for any organization to fail or perform poorly may have a variety of reasons to account for that.
These reasons may largely result from the neglect of operations strategy, too much emphasis on short-term financial performance at the expense of research and development, failing to consider customer wants and needs. Much more, when organizations neglect making investments in capital assets and human capital development, the failure to take advantage of its strengths and opportunities and the recognition of possible threats demonstrate clearly that failure is looming.
Meanwhile, the key to successful competition is to determine what the customer want and then direct efforts toward addressing their expectations. What does the customer want and the best way to satisfy those wants provide operational questions and answers to understand competitive issues that would help to work out successful strategies to meet those demands.
Again, the recognition of operations strategy as a major influencer in positioning organizations to remain competitive is not in doubt for when it is designed and executed well, there is a good chance that the organization will be successful.
What are operational strategies and Tactics?
The question to ask now is, is the failure strategic, tactical or operational issue? The answer lies with the key difference with time frame and concepts. Whereas strategy speaks to the plans and the roadmaps for reaching the destination of the organization, tactics deals with the methods and actions used to accomplish those strategies. Strategies often provide focus for decision making and tactics on the other hand ensures the provision of guidance and direction for carrying out the actual operations which need the most specific detailed plans and decision making in that organization.
To put in perspective, organization strategy deals with the overall direction for the organization whiles operations strategy relates to operations aspect of the business. To speak about operations issues is to talk about products, processes, methods, operating resources, quality, costs, lead times and schedules. To the effect, for any operation strategy to be truly effective, it is important to link it to organization strategy and with the other functional units of the organization wholly aligned.
Also, a business operational strategy is a decision making process that shapes an organization’s long-term plans to achieve the objectives in its mission statement. It comprises of specific actions management wants to take to achieve a specific aspect of the organization’s operations. Operational strategies connect the firm’s programs, policies, guidelines and workforce in a way that allows each branch to support others in achieving a common goal.
It drives the organization’s operations, the part of the business that produces and distributes goods and services. It underlies the overall business strategy which serve as critical tools for the organization to compete in an ever-changing market. With an effective ops strategy, operations management professionals can optimize the use of resources, people processes and technology to remain competitive and largely profitable.
Having said that, an effective business strategy considers a company’s long-term objectives and creates steps that cohesively bond business plans with resources, capacity, time, location and competition. When implemented successfully, operational strategies strengthen the organization’s overall strategy and may help achieve marketplace advantage over competitors.
It can also improve an organization’s competencies and infrastructure, allowing it to better serve customers and keep or even extend its competitive advantage over others in the market.
Effective Operational strategy formulation
Before creating the operational strategy, it is important to have an encompassing mission statement that defines the organization’s core objectives. This means that, there must have already been a broad mission statement that creates a clear business approach and articulates plans for achieving it. Then the organization could consider the right approach to draft a model best suited to be called its operations strategy model.
Operational Strategy Models
Great operational strategy for execution can be modelled from the following strategic underpinnings:

Learn from the best in the industry
Sometimes, the best way to beat the competition is to learn from the organizations with the best performance in the market, refining their strategies and adapt them to meet the organization’s unique goals. Operational leaders can also study organizations in other industries and even globally to learn how they create market-winning products and services, maintain their lead in competitive environments and reinvent themselves for enhanced efficiency.
Understand your market
Secondly, it is equally important that the organization knows its market and customers. Identify other products or services on the market, their unique selling points, features and benefits, the pain points they solve, pricing and customer buying habits. This information can help create products and services that can compete favorably with others at a price acceptable to its own customers and other potential ones.
Measure Performance
Again, once operational strategies have been articulated and implemented, it is essentially imperative to set them against key performance and results standards. The results may allow the organization to know what works and where it needs improvements leading to a more effective operational strategy that functions as intended.
Maintain Focus
Having mentioned about performance measurement suggest that, clear maintenance of focus is desirous. To get the best results from operational strategy, is to ensure the alignment of the different parts of the organization working together in focus of their efforts on the collective goal. Therefore, providing consistent direction with clear eye on the ball can ensure everybody is working to achieve the same objectives set out to be achieved.
Develop a unique value proposition
Besides, maintaining focus is learning and adopting industry best practices, developing a unique value proposition that distinguishes the organization’s products, services and brand from rivals. Indeed, articulating the uniqueness of its products or services to its customers can give the organization the competitive urge in the market and can equally promote and win over customers by showing them how different the organization is from its competition.
Organization strategies and the implications on operational strategies

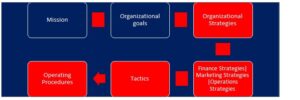
As earlier indicated, for any operational strategy to be effective, it must essentially align or flow from the overall organization objectives and strategies. This synchronized impacts affect the design and the implementation outcomes of the operational strategies. The dynamic impacts and scenario is tabled here:
Some Operational Strategies for organizational profitability and excellence.
Customer-driven operational strategy
The use of this strategy by the organizations is primarily to meet the needs of its customers. The strategy seeks to identify the trends in customer behavior such as change in buying preferences based on demographics. The data collected from the demography background of customers help the organization to adapt quickly to changes in the market by identifying the threats and the steps to mitigate them and leverage on strengths that will improve its competencies and market advantage.
Cost-driven Strategy
This strategy is designed to enable the organization compete based on price. It is common in markets where the customer may choose to buy a commodity relative to price alternatives. Owing to this, organizations decide to implement this strategy to make its cost more cost effective to offer its products a competitive price advantage.
Outsourcing Strategy
It is the norm for most organizations to rely on the expertise and supply chain resources of others to produce their products and services and deliver them to the end-user. For such organizations, there’s the need to have a comprehensive outsourcing strategy that will take care of vendor, quality control and logistics.
Competitive priorities Strategy
Organizations that adopt the use of competitive priorities strategy approach seeks to distinguish their brand, products, services and people from competitors. The strategy requires incorporating marketing strategy, production processes and organizational culture into the overall corporate strategy. The aim of this strategy is to create products and services that can always meet the needs and preferences of customers at an acceptable price point.
The strategic relevance of operational Strategy
Operational strategy involves refining and specifying an organization’s business strategy and developing strategic initiatives and operational plans, aimed at enabling departments and business units to successfully implement the overall strategy. To emphasize on the relevance of operations strategy is to admit to the significant role operational strategy plays in providing answers to the question of competitiveness and satisfaction relative to the demands of wants and needs, pricing, advertising and promotion it affords to its customers in goods and services similar to its competitors. To remain competitive as an organization is to adapt to effective strategic guide.
Moreover, operational strategy provide management with feedback regarding the overall effectiveness of the corporate and business strategies. Essentially, through operational strategy implementations, organizations are able to perform a detailed analysis to identify any omissions, problems and improvement areas needing greater attention. The advantage that it affords the organization to ensure that, implementing action plans and results are measure against predefined goals and key performance indicators cannot be overemphasized as great points for strategic relevance of operations.
Operational innovation
The term innovation is normally bandied around the retail industry but what does it actually mean? How do the industry’s leading create and interpret the term? It is important to note that what feels innovative to the retail sector may not feel innovative to other industries. I believe true innovation is only obtained when new things are experienced the first time with amazing outcomes and effects.
Admissibly, organizations either innovate or die because organizations that stand still in the face of emerging technology and disruptions in their industry will inevitably fail. The ones that adapt, pivot and collaborate with the disruption and disputes will future-proof their business and thrive.
As an approach, operational leadership combines different sets of technics to influence employees to produce creative ideas, products and services for the development and support of the organizations’ mission or vision.
The Drivers for Operational Innovation
Consequently, the changing trends in the global business world with massive technological advancements, operations leaders are expected to exhibit the behavior of associating, questioning, observing, experimenting and networking to remain innovative. Through associations, they make connections across, identify problems or ideas and ask questions to understand why and how things might be changed or disrupted.
They skillfully and carefully observe or watch customers, products, services and organizations to gain insight and ideas for the kind of change their organization expects. At the level of operational leadership, ideas are tested from diverse networks who vary wildly in backgrounds and perspectives to arrive at the best decision. Hence, by experimenting, operational leaders visit places, try new things, seek new information and experiment to learn how to innovate.
Effective innovative Leadership Behaviors

Conversely, innovation don’t just happen even with the best of organizations when operational leaders do not have the right skillsets, attitudes, behavior and the willingness to support any innovation drive. For leadership behavior to reflect the agenda for innovation drive, operational leaders must ensure:
Having said so, it important to acknowledge that, for a sustainable culture of innovation to prevail in any organization is to ensure a strict adherence to the values of the organization, providing the impetus to drive priorities and decisions, which are reflective in how the organization spends its time, money and resources.
Creating a culture of innovation demands greater investment in both human capital development, processes definition and enhancements, a conducive working climate to support the innovation drive as well as the mentality and the cultivation of the right behaviors for change. That notwithstanding, the desire and the need for innovation role models to avail themselves, prepared to articulate, explore new opportunities, encourage, support and mentor staff cannot be ruled out.
In conclusion however, I submit that, the essential elements for organizational competitiveness and the culture for excellent performance is to be strategic in the pursuit of its objectives whiles it remains operationally and culturally aligned to promote excellence and profitable organization.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
The writer is an Executive Director and the Lead Coach in Leadership Development and best Business Management practices for Discovery Leadership Masterclass.
| DISCOVERY LEADERSHIP MASTERCLASS |
CONTACTS:
|Thought Leadership | Training & Dev. |Management Consultancy |Business Conference|
Email: [email protected] or [email protected]
Tel: +233-0241824033/+233-0501324604
SPEAK. LEAD. CHANGE
23rd August, 2021










